I'm trying to extract some values in a dataframe with repeated measures based on the value in another variable.
I created 10 individual cases with 7 repeated measures in wide format to illustrate my problem. The variable n contains information about an event that happened at a specific timepoint. I would like to extract scores around that event (one before: x_n_pre1, one during: x_n, two after: x_n_post1 and x_n_post2) on different variables and save them as new variables. For simplicity I'm only including (x1 to x7) however I would also like this to also work for variables y1 to y7, ...
Knowing the variable names (or positions) in the dataframe I can do this relatively easily using case_when() , both approaches are illustrated in the code. My problem is that I also need to know the possible values of n for this approach and write a separate case_when() statement for each possible value of n.
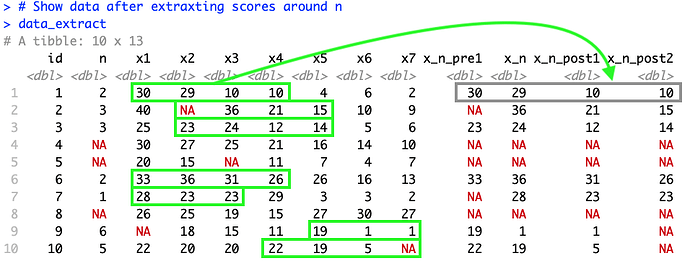
As I'm planning to use this to extract scores from different dataframes with varying numbers of repeated measurements the possible values of n will vary. Below is a screenshot of the last line of the code highlighting how I would like to rearrange the data.
I feel like it should be possible to make the code work on different datasets using some sort of iteration but I can't get my head around how. Any ideas are welcome, also completely different approaches to the one I'm describing here. Thanks ![]()
# Load packages ----
library(tidyverse)
# Create data ----
data <- tribble(
~id, ~n, ~x1, ~x2, ~x3, ~x4, ~x5, ~x6, ~x7,
1, 2, 30, 29, 10, 10, 4, 6 , 2,
2, 3, 40, NA, 36, 21, 15, 10 , 9,
3, 3, 25, 23, 24, 12, 14, 5 , 6,
4, NA, 30, 27, 25, 21, 16, 14 , 10,
5, NA, 20, 15, NA, 11, 7, 4 , 7,
6, 2, 33, 36, 31, 26, 26, 16 , 13,
7, 1, 28, 23, 23, 29, 3, 3 , 2,
8, NA, 26, 25, 19, 15, 27, 30 , 27,
9, 6, NA, 18, 15, 11, 19, 1 , 1,
10, 5, 22, 20, 20, 22, 19, 5 , NA
)
# Extract scores ----
data_extract <- data %>%
mutate(# Extract scores from one timepoint before the event n (n_pre1)
x_n_pre1 = case_when(
# If the event happend at timepoint 1, define x_n_pre1 as missing
# as x1 is the first available measurement
n == 1 ~ as.numeric(NA),
n == 2 ~ x1,
n == 3 ~ x2,
n == 4 ~ x3,
n == 5 ~ x4,
n == 6 ~ x5),
# Extract scores at timepoint n
x_n = case_when(.[ , 2] == 1 ~ .[[3]],
.[ , 2] == 2 ~ .[[4]],
.[ , 2] == 3 ~ .[[5]],
.[ , 2] == 4 ~ .[[6]],
.[ , 2] == 5 ~ .[[7]],
.[ , 2] == 6 ~ .[[8]]),
# Extract scores from one timepoint after event n (n_post1)
x_n_post1 = case_when(n == 1 ~ x2,
n == 2 ~ x3,
n == 3 ~ x4,
n == 4 ~ x5,
n == 5 ~ x6,
n == 6 ~ x7),
# Extract scores from two timepoint after event n (n_post2)
x_n_post2 = case_when(n == 1 ~ x3,
n == 2 ~ x4,
n == 3 ~ x5,
n == 4 ~ x6,
n == 5 ~ x7,
# If the event happend at timepoint 6, define x_n_post2 as missing
# as there are only 7 repeated measurements in the dataset
n == 6 ~ as.numeric(NA)))
# Show data after extraxting scores around n
data_extract
#> # A tibble: 10 x 13
#> id n x1 x2 x3 x4 x5 x6 x7 x_n_pre1 x_n
#> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 2 30 29 10 10 4 6 2 30 29
#> 2 2 3 40 NA 36 21 15 10 9 NA 36
#> 3 3 3 25 23 24 12 14 5 6 23 24
#> 4 4 NA 30 27 25 21 16 14 10 NA NA
#> 5 5 NA 20 15 NA 11 7 4 7 NA NA
#> 6 6 2 33 36 31 26 26 16 13 33 36
#> 7 7 1 28 23 23 29 3 3 2 NA 28
#> 8 8 NA 26 25 19 15 27 30 27 NA NA
#> 9 9 6 NA 18 15 11 19 1 1 19 1
#> 10 10 5 22 20 20 22 19 5 NA 22 19
#> # ... with 2 more variables: x_n_post1 <dbl>, x_n_post2 <dbl>
Created on 2018-12-03 by the reprex package (v0.2.1)
Session info
devtools::session_info()
#> ─ Session info ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> setting value
#> version R version 3.5.1 (2018-07-02)
#> os macOS 10.14.1
#> system x86_64, darwin15.6.0
#> ui X11
#> language (EN)
#> collate en_GB.UTF-8
#> ctype en_GB.UTF-8
#> tz Europe/London
#> date 2018-12-03
#>
#> ─ Packages ──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
#> package * version date lib source
#> assertthat 0.2.0 2017-04-11 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> backports 1.1.2 2017-12-13 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> base64enc 0.1-3 2015-07-28 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> bindr 0.1.1 2018-03-13 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> bindrcpp * 0.2.2 2018-03-29 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> broom 0.5.0 2018-07-17 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> callr 3.0.0 2018-08-24 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> cellranger 1.1.0 2016-07-27 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> cli 1.0.1 2018-09-25 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> colorspace 1.3-2 2016-12-14 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> crayon 1.3.4 2017-09-16 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> desc 1.2.0 2018-05-01 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> devtools 2.0.1 2018-10-26 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.1)
#> digest 0.6.18 2018-10-10 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> dplyr * 0.7.8 2018-11-10 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> evaluate 0.12 2018-10-09 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> fansi 0.4.0 2018-10-05 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> forcats * 0.3.0 2018-02-19 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> fs 1.2.6 2018-08-23 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> ggplot2 * 3.1.0 2018-10-25 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> glue 1.3.0 2018-07-17 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> gtable 0.2.0 2016-02-26 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> haven 2.0.0 2018-11-22 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> hms 0.4.2 2018-03-10 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> htmltools 0.3.6 2017-04-28 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> httr 1.3.1 2017-08-20 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> jsonlite 1.5 2017-06-01 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> knitr 1.20 2018-02-20 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> lattice 0.20-38 2018-11-04 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> lazyeval 0.2.1 2017-10-29 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> lubridate 1.7.4 2018-04-11 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> magrittr 1.5 2014-11-22 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> memoise 1.1.0 2017-04-21 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> modelr 0.1.2 2018-05-11 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> munsell 0.5.0 2018-06-12 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> nlme 3.1-137 2018-04-07 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> pillar 1.3.0 2018-07-14 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> pkgbuild 1.0.2 2018-10-16 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> pkgconfig 2.0.2 2018-08-16 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> pkgload 1.0.2 2018-10-29 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> plyr 1.8.4 2016-06-08 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> prettyunits 1.0.2 2015-07-13 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> processx 3.2.0 2018-08-16 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> ps 1.2.1 2018-11-06 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> purrr * 0.2.5 2018-05-29 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> R6 2.3.0 2018-10-04 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> Rcpp 1.0.0 2018-11-07 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> readr * 1.2.1 2018-11-22 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> readxl 1.1.0 2018-04-20 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> remotes 2.0.2 2018-10-30 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> rlang 0.3.0.1 2018-10-25 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> rmarkdown 1.10 2018-06-11 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> rprojroot 1.3-2 2018-01-03 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> rvest 0.3.2 2016-06-17 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> scales 1.0.0 2018-08-09 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> sessioninfo 1.1.1 2018-11-05 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> stringi 1.2.4 2018-07-20 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> stringr * 1.3.1 2018-05-10 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> testthat 2.0.1 2018-10-13 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> tibble * 1.4.2 2018-01-22 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> tidyr * 0.8.2 2018-10-28 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> tidyselect 0.2.5 2018-10-11 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> tidyverse * 1.2.1 2017-11-14 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> usethis 1.4.0 2018-08-14 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> utf8 1.1.4 2018-05-24 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> withr 2.1.2 2018-03-15 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> xml2 1.2.0 2018-01-24 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#> yaml 2.2.0 2018-07-25 [1] CRAN (R 3.5.0)
#>
#> [1] /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/3.5/Resources/library

 I tried to find a solution for quite some time now. Great idea to create the index and then use case_when, thanks!
I tried to find a solution for quite some time now. Great idea to create the index and then use case_when, thanks!