Estimated Nuclear Warhead Inventories, 2023
Authors: Sukalpo Saha
github
linkedin
twitter
Full Description:
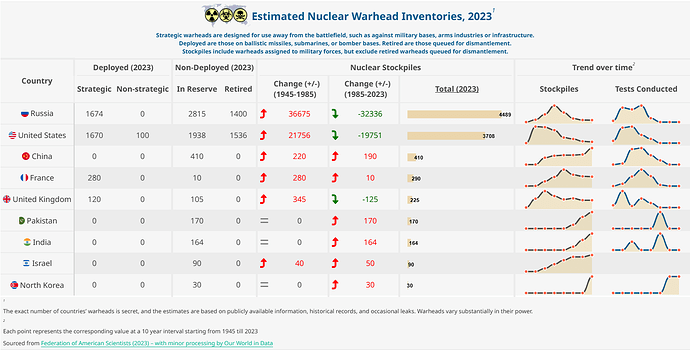
Nine countries currently have nuclear weapons: Russia, the United States, China, France, the United Kingdom, Pakistan, India, Israel, and North Korea. These nuclear powers differ a lot in how many nuclear warheads they have. The Table shows that the warheads differ in how — and how quickly — they can be used: some are designed for strategic use away from the battlefield, such as against arms industries or infrastructure, while others are for nonstrategic, tactical use on the battlefield. And while some warheads are not deployed, or even retired and queued for dismantlement, a substantial share of them is deployed on ballistic missiles or bomber bases and can be used quickly.
After increasing for almost half a century after their creation in the 1940s, nuclear arsenals reached its peak in the 1980s. Since then, we have seen a reversal of this trend, as the table shows. The nuclear powers reduced their arsenals (also number of nuclear tests conducted per year) a lot in the following decades, and the total number of warheads across all countries fell below 20,000 in the 2010s. The decline has slowed since then, and the total stockpile still consists of more than 10,000 warheads. Some countries have also been expanding their arsenals.
Bastian Herre, Pablo Rosado, Max Roser and Joe Hasell (2024) - “Nuclear Weapons” Published online at OurWorldInData.org.
Retrieved from: 'https://ourworldindata.org/nuclear-weapons' [Online Resource]
Table Type: static-HTML
Submission Type: Single Table Example
Table: Nuclear Weapons
Code: GitHub - ahasoplakus/nuclearweapons: Nuclear Weapon Inventories, 2023
Language: R
Industries: public-sector.
Packages: gt, gtExtras