A short history of working time in Austria
Authors: Matthias Schnetzer
Read the closeread article: Eine kurze Geschichte der Arbeitszeit
Reproducible repo: GitHub - mschnetzer/scrollytell_arbeitszeit
Abstract
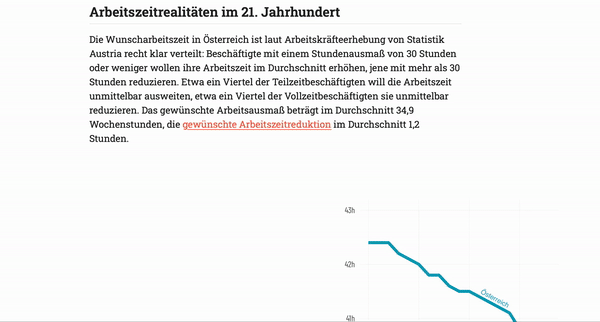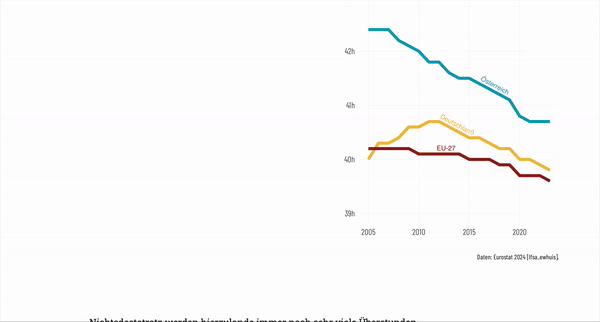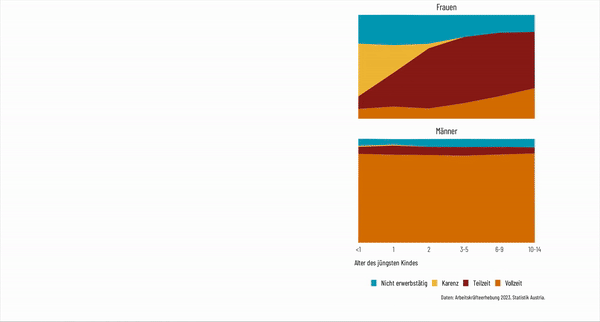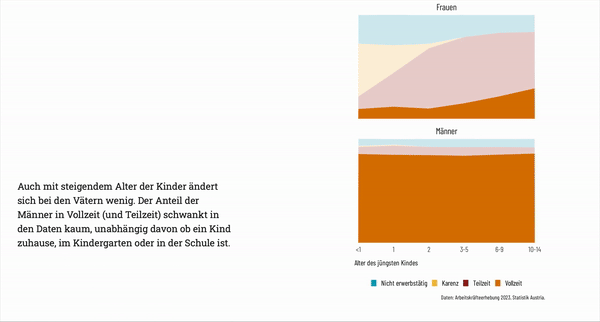
The website presents the evolution of work time regulation and current figures on working time in Austria. First, it shows a brief history of the eight-hour working day before turning to recent developments of working time. The figures show the reduction of average full-time working hours in recent years, the share of unpaid overtime, the gender-specific division of labour in families, and the provision of public child care.
The website is published in German.
Full Description
This webpage provides an interactive, visually engaging history of working time in Austria, spanning from the 19th century to the present day.
Overview
The page opens with a historical perspective on Austrian working hours, starting in the industrial revolution when workdays ranged from 12 to 16 hours. It shows how the labor movement, driven by worker protests and social reforms, achieved milestones such as the 8-hour workday by the early 20th century. This section highlights the gradual but significant evolution of labor laws as they adapted to changing economic conditions and social expectations.
8-Hour Day and Beyond
A major turning point was the adoption of the 8-hour day and 48-hour workweek, following international labor standards and worker advocacy. The page illustrates how these early victories shaped Austria's labor landscape and prepared the ground for further reductions in working hours. Moving into the post-war period, the presentation describes how economic growth, social change, and technological advancements paved the way for a 40 hours workweek in the 1970s.
Gender Inequality in Unpaid Labor
The webpage emphasizes Austria's ongoing gender disparity in unpaid labor. Women perform most unpaid domestic and caregiving work, and this gap persists despite the formal reduction in average paid working hours.
Part-Time Employment and Care Infrastructure
A section focuses on the high rate of part-time employment among Austrian women, often due to insufficient childcare options. The page discusses the challenges women face in balancing work with family responsibilities, as well as the societal impacts of limited public childcare.